Problems Growing Pear: 5 Causes of Curling and Blackening of Leaves
Pear is one of the most common fruit trees in summer cottages. Often gardeners are faced with a sudden blackening, twisting of its foliage, which leads to the death of a tree. Because of what diseases and other factors such a problem appears, we will understand in this article.
The most dangerous and common disease of a pear is considered a bacterial burn. The problem is that the disease does not stop at one instance, infecting all surrounding plants.
Causes and signs of the disease
The causative agent of an infectious disease is group of enterobacteria(eg salmonella). The affected areas of the plant, as the disease develops, secrete a certain yellowish substance, which contains a whole settlement of harmful microorganisms.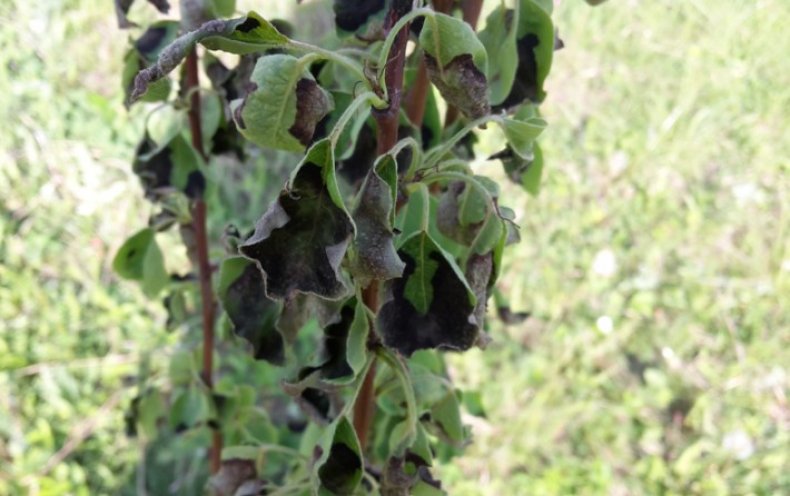 
Symptoms of disease damage:
- the petals of the inflorescences fade and fly around, the pedicel changes its color first to bright green, and then to the color of light amber;
- as it spreads, the kidneys are affected, although they do not fall off, they darken and lose their functions;
- the leaves do not fly around, but turn black with whole rosettes;
- the affected branches also acquire a dark color;
- penetrating through cracks in the bark, the disease infects the trunk, the bark dries out, turns brown and forms dead zones. With such necrosis, discharge of a liquid milky substance is noticed.
Did you know? Sailors of ancient Greece with the help of a pear fought against nausea and seasickness.
What to do
It is always easier to prevent than to treat, so first let's talk about preventive measures for a bacterial burn. So to reduce the risk of disease the following must be remembered and taken into account:
- weeding (weeds can be infected);
- for any planting and procedures in the garden, it is imperative to use only clean equipment intended exclusively for the garden;
- wild fruit trees located near the site should be uprooted;
- do not ignore regular garden insecticide treatments.

Measures to combat existing foci of infection:
- streptomycin;
- tetracycline;
- ofloxacin.
These drugs should be used strictly according to the instructions, you need to spray all the affected areas: inflorescences, leaves, shoots and plant stem. Carry out the spraying procedure in cloudy calm weather.
An effective remedy is also a solution with lime. It should be noted here that increased dosages can lead to a chemical burn of the foliage.
Important! If treatment with drugs does not lead to a healing effect, the diseased tree must be uprooted and disposed of. The tools used in this case are sterilized with formalin or carbolic acid.
Video: treatment of pear bacterial burn
pear scab
Scab is an infectious disease, the pathogens of which can overwinter on the affected shoots, fallen leaves. The spread of the disease largely depends on weather conditions.
Did you know? The Chinese are firmly convinced that it is impossible to share one pear with friends or lovers, otherwise it will lead to a quarrel and parting.
Why and how it appears
The infection is caused by fungi that are active in a humid environment. It is noteworthy that the fungus can also appear in dry, hot weather in the presence of heavy dew.
Symptoms of infection indicate dark spots with a fluffy coating that look like mold spots. As the disease progresses, the foliage turns black, tissues are destroyed, which leads to leaf fall. In the future, the scab also affects the branches, covering them with a dark, brown hue with a crust. Without adequate treatment, the fruits are affected, covered with black dots.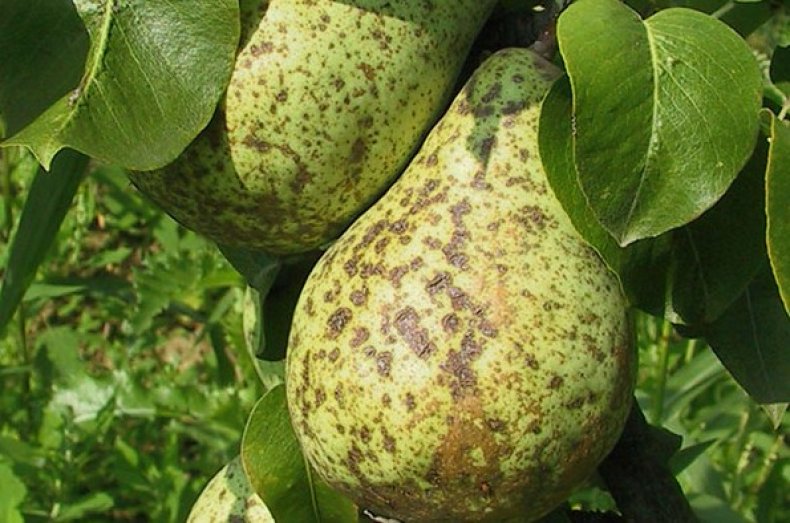 
How to treat
At the first symptoms, spraying is an effective treatment. Due to the short action of the drug (14 days), the treatment is carried out up to seven times per season. The first procedure is carried out before the buds open.
Systemic drugs:
The duration of action of the drugs is from 20 to 35 days, the treatment is carried out twice a season, the drugs are not washed off by rain.
Video: processing pear and apple trees from scab with fungicidal preparations
In combination with treatment with drugs, foliar top dressing is carried out with one of these fertilizer:
- (10% concentration);
- (10%);
- (from 3 to 10% concentration);
- (3-10%);
- (5-15%);
- (5 -10%).
Prevention measures:
- timely pruning (dense crown is an ideal environment for fungi);
- cleansing the near-stem circle from fallen leaves and weeds;
- in it is recommended to keep the trunk circle under black steam;
- in the spring, a prophylactic drug "Agate" or a similar agent is carried out.
Lack of elements and blackening of leaves
Blackened pear leaves may be a reaction to a lack of certain minerals. 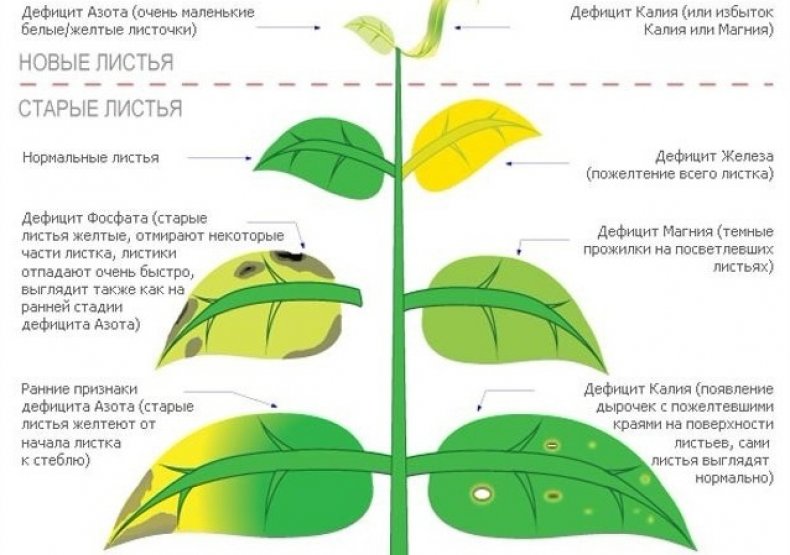
Let's take a closer look:
- potassium. The edges of the leaf plates begin to dry out, forming a kind of dark-colored border, the plate itself wrinkles and changes shape. The lack of a mineral is clearly visible on the lower, older branches;
- iron. Foliage growth slows down, chlorosis is observed, not only the leaves dry out, but also the tops of the shoots. The tree begins to shed its leaves, the quantity of the crop decreases, and its quality deteriorates. Young shoots of the current year suffer the most;
- zinc. The lack of a mineral causes drying and darkening of the foliage. During the fruiting period, the fruit becomes smaller, its peel changes its structure, becoming covered with dense patches and dark spots. Foliage and branches are deformed;
- calcium. Foliage with a lack of calcium is prone to burns, becomes covered with dark spots, curls. The taste of fruits worsens, under the skin the flesh is affected by spotting, the shelf life of fruits decreases;
- phosphorus. The leaf plate changes shape, stretching in length, darkens. Young shoots stop growing, deform. Foliage on old shoots flies around;
- copper. The lack of this element in the soil is extremely rare, mainly on peat soils, less often on sandy and soddy soils. The deficiency is manifested by darkening and twisting of the leaves, drying out of young shoots and the top of the tree.
Distinguish three kinds of insect: spotted, red and yellow sucker. Most often, adults hibernate on a tree, breeding offspring in the spring. The insect lays eggs in the bark of shoots, and later on swelling buds and foliage.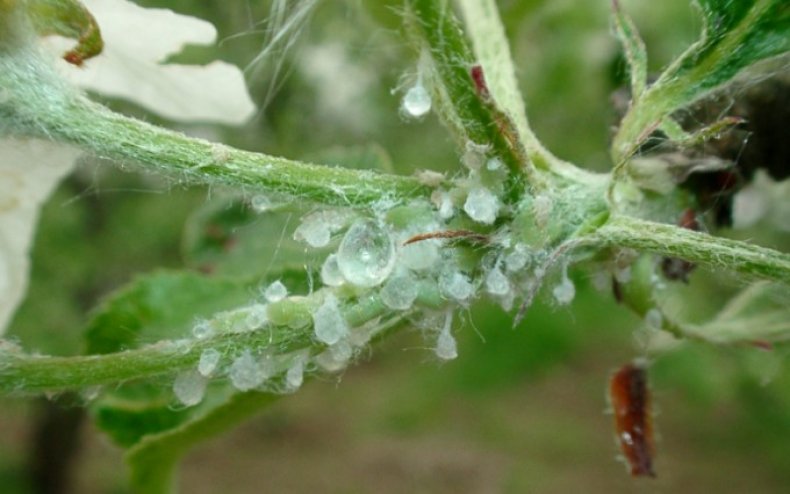  The first destruction procedure is carried out in early spring, when the temperature is above zero during the day, always on a sunny, calm day. Use such drugs:
The first destruction procedure is carried out in early spring, when the temperature is above zero during the day, always on a sunny, calm day. Use such drugs:
- "Sherpa";
The first procedure destroys adult insects, the subsequent ones carried out before and immediately after flowering kill the larvae. When re-spraying, for example, Dimilin is used.
- (2%) or before bud break begins;
- "Keltan" (20%) or (10%) during the period of formed buds;
- or (0.1%) after flowering.
Important! The solution is prepared according to the instructions for the drug, if necessary, spraying is repeated at intervals of ten days.
- infusion: 3-4 kg of fresh or 1 kg of dried raw material is poured with 1 bucket of water, covered with a lid and infused in a warm place for 36 hours;
- infusion: 400 grams of roots (or 600 grams of leaves) are infused for 3 hours in 10 liters of water;
- onion infusion: 200 grams are poured into 10 liters of water and infused for 12-15 hours;
- soap solution: 300 grams of laundry soap for all the same 10 liters of water.
Video: processing fruit trees from aphids with ammonia




