Growing grapes: planting, propagation, care, feeding
Growing grapes on your site is not the easiest task that a gardener sets for himself. Cultivation of this crop should be taken seriously . Shelter, watering and fertilizing of grapes must be done in a quality and timely manner., and then a rich harvest will not keep you waiting.
First of all, when laying a vineyard, it is necessary to choose a variety that is suitable for the climatic conditions of the region. Then you should pay close attention to the acquisition of high-quality planting material. You can buy it or grow it yourself. In the absence of experience, it is advisable to use purchased seedlings purchased from proven, well-established nurseries.
Choosing planting material
First of all, evaluate the appearance of seedlings. The leaves should be green and fresh, with no signs of overdrying. The stem is strong and resilient, covered with brown bark, without visible wounds and growths. When planted, such grapes will quickly take root and grow.

A quality young vine cannot be lower than 50 cm. A well-developed root system has at least 3-4 branches. It is better to buy plants with closed roots, in a container or pot. If the buds have not yet blossomed, then the quality is determined by them. The dry, flaky surface of the integumentary scales is a reason to think about whether the seedling was stored in good conditions? Most likely, he is already weakened, and there is no point in investing in his cultivation.
Ask the seller what fertilizers were applied under the grapes, and how many times. If there were more than 4-5 top dressings during the growing season of the seedling, then the plant already depends on them. It needs to be adapted to the normal life cycle. At first, you will have to feed intensively, as in a nursery, and then gradually reduce the rate of fertilization.
Propagation of grapes by cuttings
winter distillation
This method is most often used by gardeners expanding their vineyard. It consists in the fact that in the fall, when pruning, cuttings are harvested and placed in a jar of water. The kidneys must not fall into the water. If the length of the trunk does not allow to protect the kidneys from contact with the liquid, then they are cut off. Closer to mid-January, new roots appear, and then the plant wakes up. In mid-March, cuttings with roots must be transplanted into pots and grown on the window. When planting, they can be watered with the growth stimulator "Epin", or "Hom". It is advisable to sometimes spray the leaves, as steam heating dries the air in the room, creating not the most comfortable conditions for the plants.
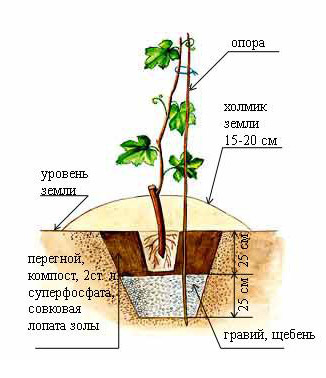
planting grapes
Overwintered cuttings
Planting material is harvested in different ways. For example, autumn cuttings are not brought into heat, but left to winter on the site. So that in winter they do not freeze, a trench is dug for them, and the cuttings are dug in it until the onset of spring. They come to life beautifully, and quickly take root after such stratification.
Also, dormant grape seedlings can be stored in the cellar or in the refrigerator in winter. They are periodically checked and sanitized - wiped with a solution of potassium permanganate to prevent mold. In the spring, the cuttings are rooted and transplanted to a permanent place.
Video: propagation of grapes by cuttings
Seedlings from the stone
You can try to propagate the variety you like at home by planting a bone in a pot with soil. This must be done in advance, as it can hatch for several months. Therefore, autumn planting is recommended. There is a way to hasten the spitting of the seed - it is soaked in a damp cloth for about a month. The cloth must be rinsed every three days, otherwise pathogenic microflora will form on it. In the spring, after the onset of warm days, a small vine is transplanted to a permanent place, and they grow it there, without pruning, for several years, until the first fruiting.
Growing in the middle lane
Despite the fact that many consider the cultivation of grapes the prerogative of the inhabitants of the southern regions, it can be planted in cooler climates. For example, in the Pskov, Leningrad, Kirov and Novgorod regions, many summer residents successfully grow both covering and non-covering varieties. Each of them has its pros and cons, but most importantly, with proper care and timely feeding of grapes, you can get quite a decent harvest from both varieties.
Covering varieties
A prerequisite for the wintering of these grape varieties in regions with a temperate climate is the construction of shelters over them. To do this, you can use roofing material, or a black film, in general, any material that does not allow moisture and light to pass through. This method is used if the grapes are cut short enough. But long vines are insulated in a different way. Above them, a frame is constructed from greenhouse arcs of small radius, and covered with several layers of polyethylene film. For this purpose, you can use other improvised materials, for example, wooden boxes. In the spring, melt water can get under the grapes, and it can rot. To avoid such a nuisance, ventilation is necessary. To do this, the covering material is lifted during the day and propped up with sticks or bricks so that the soil under the plant can dry. And at night the vine is covered again.

After the onset of stable warm weather, the shelter is finally removed, and the vines are pruned. For faster development, grapes are watered with growth stimulants. For example, you can use .
By the way, you can start feeding the grapes even before he woke up. In early spring, when there is still snow, granular is scattered around the entire radius of the trunk hole. Application rate - about 40 g per sq. m. Since phosphorus belongs to a class of fertilizers that are difficult to digest, its early application is very natural. Until the moment when the long-awaited heat comes, this “slow” element will be able to move from the granules to the soil complex, and will be ready for absorption by the roots of the plant.
So, after we have taken care of the "awakening" of the vine, and stocked up phosphorus for the future, it is necessary to think about feeding the grapes with other necessary elements. In May, the plant will need nitrogen to form and build up green mass. Therefore, after the buds swell, the vines are watered. It contains a large amount of the macronutrient nitrogen, as well as many microelements, such as magnesium, which are necessary for grapes for full-fledged qualitative development. It is prepared as follows - 1 part of the liquid substrate is mixed with two parts of water, and set to ferment in a warm place for a week. After that, the working solution is diluted in a ratio of 1:10, and the grapes are watered, spending about a liter per plant. This solution should not be poured under the root. It is better to make a groove around the circumference of the hole, and pour fertilizer into it. Then the earth is leveled, and watered abundantly with plenty of water.
Berries appear on the grapes in July, which in temperate climates often grow not too sweet. This is mainly due to the fact that the grapes do not have enough heat, because at high temperatures vegetable sugar is better synthesized. This disadvantage is compensated by feeding the grapes with a variety.
Video: pruning and sheltering grapes for the winter
Uncovered varieties
Unfortunately, these easiest-to-grow and most hardy varieties, when moving to the northwest, often do not withstand local weather conditions, and again, they have to be covered. But for a shorter period than those that are officially considered covering. That is, not for the whole winter, but only in the spring, in April-May, with a special material spandball, which protects already blossoming buds from recurrent frosts. The harvest of non-covering grapes ripens only in September.
In connection with this feature, the grape fertilization schedule is shifting. In April and early May, the vine of a non-covering variety is only ventilated without adding anything under it. Nitrogen, which is the starting element of growth, is introduced at the end of May under the root, in the form of extracts from animal organic matter. For their preparation, you can use chicken manure, lamb or.

Mineral fertilizers are used in combination with natural fertilizers, alternating their application. If nitrogen supplementation was of animal origin, then agrotuk is used further. At the end of June, phosphate fertilizers are applied, it is possible in combination with nitrogen, for example, azofoska. The rate of use is 20 g per 1 sq.m.
In late July - early August, they begin to introduce potassium in the form of foliar top dressing. For example, you can use this recipe (for 10 liters of water):
- - 1 l;
- Sugar - 3 tbsp. l;
- Boron - 1g;
- Copper - 1.5 g.
Also potash fertilizers are also applied under the root. They help grapes in the synthesis of vegetable sugars, which, in turn, affects the taste of berries. In addition to loose mineral fertilizers, ready-made mixtures with a balanced composition are also used. You can buy them at any gardening store. The best, according to the reviews of practicing winegrowers of the middle lane, can be considered "Clean Leaf", "Biochelate", "Master" with NPK 15:5:30.
Video: seminar on growing grapes in the middle lane
Growing grapes in the northern regions
Previously, in these regions, grapes were not cultivated at all, as they believed that this was a hopeless occupation. The average annual sum of positive temperatures in the cold regions of our country is so small that it would seem that it is not even worth trying. But there were enthusiasts who tried. It did not work out right away, but the great desire of gardeners to adapt grapes to almost extreme conditions won, and they developed several ways to grow it in the northern regions.
For example, in Tyumen such early and super early varieties grow as Super-Extra, Julian, Victor, Galahard, Brilliant. They are grown there exclusively in greenhouses with a removable roof., cover very well in winter. Another option for the north is to grow grapes in tubs, and for the winter period, transfer the plants to the basement, where the minimum positive temperature is maintained so that it can “rest” in the winter, but does not freeze out.

The main problem of northern grape varieties is tasteless and small berries.. They do not have enough heat and sun to synthesize enough vegetable sugars. The situation can be corrected with the help of fertilizers for grapes. They are brought in at the time of boarding. The following soil mixture recipe is recommended:
- Sod land - 10l;
- River sand - 10 l;
- Clay yellow - 5 l;
- Styrofoam (crumb) or hydrogel (granules) - 5l;
- Superphosphate simple powder - 30 g;
- Wood ash - 30 g;
- - 20 g;
- Dolomite flour - 10 g.
Such an original ingredient as polystyrene is included in this list for a reason. Grapes need well-drained soil that does not stagnate with excess moisture. Otherwise, the roots of the plant begin to rot, and it dies.
Grapes growing in barrels need to be fed as often as those growing in the open field, but the concentration of fertilizers must be reduced. It is fed with all popular fertilizers for grapes. Chicken manure is considered the best nitrogen-containing top dressing for the vine.
An earth ball limits the amount of macro and microelements that can be applied to plants. It is most convenient to use chicken manure pellets, which can be purchased at specialized garden centers. Under one vine, depending on its age and the volume of the container in which it grows, you can apply from 70 to 10 g of this granular fertilizer, slightly deepening it into the ground. After top dressing, abundant watering is necessary.
Video: growing grapes in northern latitudes
Grapes are considered a capricious plant, but, as practical experience shows, it can be grown anywhere. By adhering to the basic rules of care, not forgetting about fertilizers for grapes, you can get beautiful berries in all regions of the country, and surprise your neighbors and friends with harvests.




