How to get rid of fungus on indoor plants. Chemical means of combating fungal diseases. downy mildew
Fungal diseases are dangerous because they are poorly diagnosed, some of them are difficult to treat and at the same time spread very quickly. Often the affected plant has to be destroyed. Therefore, it is imperative to use preventive measures. The fungus loves weakened specimens, high temperature and humidity. The source of infection can be soil, dust and newly acquired plants.
One of the most common problems on pomaceous is the proliferation of fungal or cryptogamous diseases, most commonly referred to as "mildews" due to the appearance of their fruits, which usually cover the attacked plant. These pathogens, if not timely fought, can quickly destroy flowers and fruits, thus plant production; favor wet or rainy climatic conditions, and they mainly affect nutritionally deficient body fat.
The symptoms of affected organs are various, they can be mold, rot, gums, bulge, sekumi, the following table shows the symptoms and causes. Poverty of fruit plants. Believing that in the fight against plant disease "prevention is the best medicine" and that " good food is the best resource for disease resistance", we will look at the second part of the pathologies affecting a group of droids.
The most common fungal diseases are:
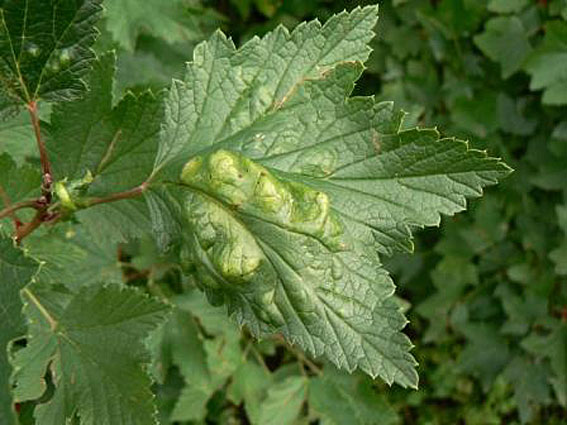

Prevention measures
Fungal diseases are easier to prevent than to treat. Therefore, it is necessary to observe certain preventive measures when caring for plants:
- Compliance sanitary norms at work;
- Watering and spraying are carried out using clean water;
- Tools, containers and soil must be disinfected;
- Excessive soil moisture is not allowed;
- Carrying out periodic inspection of plants for the presence of pests;
- Regular ventilation of the room.
This fruit trees, which, with a limited initial distribution, expanded rapidly with the introduction of new selections such as dwarf nectar peaches, early cherries, or Sino-Japanese-type midget plums. These are reasons favoring cultural interest, sometimes expanding the culture beyond their ideal area of acclimatization, with particular emphasis on the cold requirements and the difficulty of fertilizing them.
Thus, the success of villus cultivation is a combination of ideal conditions such as establishment, proper management of fertilization and defense, and also, as in the case of other cultures, it is important to constantly monitor one's condition in order to be able to adequately intervene contain the spread of pathologies and encourage proper development.
Bacterial diseases
The causative agents of bacterial diseases of plants are bacteria that penetrate through damaged areas of the skin and begin to spread throughout the vascular system. Currently, there are no effective drugs for the treatment of diseases of this type.
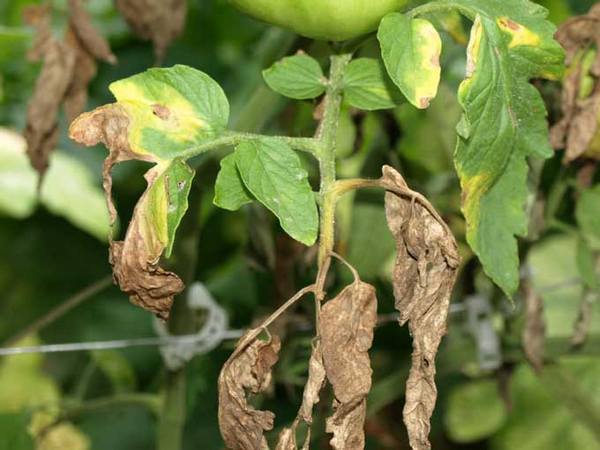

Treatment and prevention measures
Bacterial diseases of plants are very difficult to treat, and sometimes simply impossible. And it is very easy to transfer them from one plant to another. Therefore, when carrying out work, it is necessary to constantly disinfect the tool and hands. Planting pots that have been in use should be kept in boiling water for some time.
All redwood trees need neutral to acidic soil rich in fertilizer, organic matter and adequate moisture to grow, thrive and produce on a regular basis. Lack of suitable soil for cultivation and lack of nutrients causes general plant decay with poor flowering and therefore poor production, and leaf yellowing associated with various pathogens.
Food deficiencies negatively affect the entire physiology of the plant, primarily reducing their resistance to disease control, and in the specific fruit sector, the damage is reflected in the economy due to the lack of production, the low quality of fruits and the low conservatism of the same.
Treatment of bacterial diseases is possible only at the very beginning of their development. All foci of infection are removed with a part of healthy tissue. After that, the remaining parts are sprayed and watered using Bordeaux mixture and other disinfectants containing copper. If this does not help, the plant is subject to complete destruction.
Depending on the type of nutrient the plant is deficient in, the following main causes are listed in the table below. These pathogens, if not fought in time, can quickly destroy flowers and fruits and therefore produce plants, and preference is given to humid or rainy climates and is more prone to nutrient deficiencies in the grouse.
These manifestations are rooted in the plant, and usually only certain organs are preferred by different pathogenic groups, and therefore localization allows us to diagnose them. The symptoms of affected organs are various, they can be mold, rot, cancer, gums, bulge, sekumi, the following table shows the symptoms and causes.
Viral diseases
Viral diseases are less common than fungal and bacterial diseases, but they are more dangerous. The ways of infection with the virus can be very diverse: mechanical damage during transplantation, garters, vaccinations; its transfer during work from an infected plant to a healthy one; entry by pest bites.
In this third part, dealing with the problems of fruit plants, we will look at the main causes of damage to the wine and table vine, and will indicate the main symptoms with useful remedies for the proper cultivation of this plant, among the most common at an agricultural and amateur level. The success of growing grapes, like all plants, is the result of a set of ideal balance conditions, including: agronomic technique, proper management of fertilization and protection, and, like other crops, constantly making sure they were able to intervene in a timely manner to contain the spread of pathologies and encourage proper development.
Determining the presence of a viral disease is very difficult, since the signs are very similar to other plant diseases (withering, decay, and others). This can only be done with special analyzes. All viral diseases are divided into two large groups.
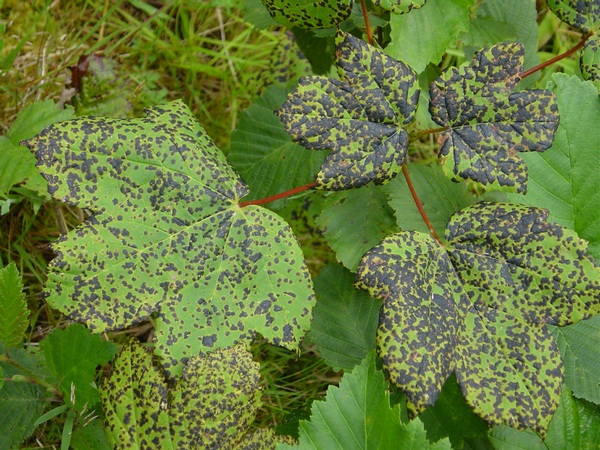

Important! Viral diseases of plants completely affect the vascular system, therefore, on this moment have no treatment. Affected plants can only be destroyed.
General rules that are already provided for dealing with the adverse effects of other cultures, such as "prevention, is best care", and that "good nutrition is the best resource for disease resistance" is more than important in viticulture and for this reason Recognize from the earliest symptoms pathogens or the cause of a group of vegetative blocks unfavorable causes in tables with diseases and damage caused. To illustrate the various problems that damage the vine, the various causes can be grouped into: environmental, parasitic, fungal, insect and animal damage.
Diseases caused by improper care
TO improper care Plants are primarily:
- Excess or lack of moisture;
- Incorrect content temperature;
- Increased humidity or dryness of the air;
- Excessive or insufficient top dressing;
- Wrong light mode.
All screws, in order to be able to grow and produce regularly, need neutral, well-drained soil, discreetly equipped with fertilizer, organic matter, and moisture in temperate soil. Although the grapevine is a rustic species, due to the lack of suitable growing soil and lack of nutrients, this causes a general depletion of the plant, the consequences of which negatively affect the entire physiology of the plant, reducing the production and quality of the product for food products if table grapes or oenological value are used and preserved if wine is being produced.
Continuing the conversation about pesticides, consider a group of fungicides. These are chemicals that fight fungal plant diseases. Before turning to the characteristics of these drugs, let me remind you that eradicating diseases is much more difficult than limiting the harmful activities of insects. Therefore, pay special attention to disease prevention in advance.
Depleted plants for nutritional deficiencies are most often affected by parasites as their disease-fighting resistance is reduced. Deficiency vessels show certain symptoms such as yellowing, reddening of leaves, flowering and poor attachment, or bunches with small, misshapen and tasteful acorns.
The vine is easily attacked by various fungal or cryptogamic diseases, most commonly referred to as "molds", due to the appearance of their fruit trees, which usually cover the attacked plant. These pathogens favor wet or rainy climates and if not controlled in a timely manner, they can multiply, destroying leaves, flowers and clusters with productive and high quality droplets in a short time.
According to the mode of action, they can be divided into preventive and therapeutic.
Preventive drugs act on the initial stages of fungal development that occur on the surface of the plant. If the fungus penetrates into the middle, it becomes inaccessible to the action of drugs.
For the most part, contact fungicides are preventive. For their high-quality work, it is necessary that the plant be completely and evenly covered with the preparation, but with the growth of young shoots, they will no longer be protected from the disease. In addition, these drugs are washed off by rain, for these reasons, the duration of their protective action may be reduced.
Manifestations are more severe on nutritionally deficient vines and, depending on the different groups of pathogens, they differ in symptoms and organs affected: mold, rot, cancer, sekumi; the following table shows the symptoms and causes. Colorful and beautiful can't be easy autumn leaves on trees, but plant leaves can also vary throughout the year. There are many varieties of houseplants that we admire for the beauty of their flowers, but only for their beautiful leaves.
It can literally be a visual magnet in any space. They offer beautiful and often unconventional colors, interesting textures, and sometimes incredible vein patterns. Stripes, colorful spots, bright ribs, interesting veins, lingering, unusual structure, we can all charm the leaves of some houseplants, more than the beauty of flowers, admire the beauty of the leaves. These plants deserve enough space in the interior. They can reliably rotate the color palette of almost every color of the rainbow.
Therapeutic fungicides inhibit or stop the development of the disease, penetrating into the middle of plants and acting on the pathogen, even when it has begun to grow and develop. Such drugs have a systemic and translaminar effect, that is, the ability to penetrate the leaf cuticle and accumulate inside plant tissues. The word has Latin roots: trans (trans) - through, through, beyond; lamina (lamina) - a plate, a strip. And if you translate the word literally - this is penetration through the skin.
How do leaves get their beautiful colors?
The beauty of their leaves in many ways distinguishes the beauty of flowers. It's hard to believe that the beauty of the color of so many deliciously colorful leaves is actually a disease. Poor development, especially in yellow and white fluted petals, is actually well known for timping. In the case of plants, there is a lack of chlorophyll, which leads to significantly less green areas on the leaves. For other species, such as colorful maples, their variegated colors are viral. In the case of such diseased plants, their progeny is also bright if we multiply the plant with cuttings.
Systemic action is the ability of substances to spread in tissues and move through them as the plant grows.
Such fungicides do not depend on precipitation and have a long-term protective effect. However, it should be remembered that no matter how effective fungicides are, they should be used before the appearance of external signs of the disease or at the first symptoms of it.
However, if we choose to sow seeds, the new plants will be healthy and therefore will have green color. There is enough light for the plants to keep their stunning, interesting leaf color, otherwise many of their wonderful impressions may be lost. In the shade or in the dark, plants are forced to produce large quantity chlorophyll, which leads to green leaves. Only green leaves can capture and use the incident light.
The most beautiful - young plants
We do not retain the praise of these plants in general, but it is certainly fair to acknowledge the negative ones. In addition to blooming or not blooming, it still remains a fact that among creeping homeowners there are many whose beauty decreases with increasing number of years. This is especially true for African nettles and Iresina, which is a great shame. But on the other hand, it is very easy for these plants to propagate cuttings to grow new young beautiful and brightly colored rooms.
Quadris
Quadris is a systemic fungicide that protects vegetable crops from major diseases, that is, it has a fairly wide spectrum of action. It has translaminar and systemic action. A feature of Quadris is that it lengthens the fruiting time of vegetable crops by 2-3 weeks.
Important! If the drug is treated before harvesting, this significantly improves the keeping quality and safety of vegetables when stored at home and in storage.
The visitor group includes about 10 species whose home is mainly the Amazon basin. Representatives of these species mainly like moist and shady habitats. It should be noted that grass poisonous plant because it is classified as an arachnid. But the beauty of the colorful pattern of its leaves doesn't give you much room to think about its toxicity. From the spring months through the entire growing season, do not treat it with a dressing or fertilizer. Old plants produce lateral tubers that can be used to grow new plants.
Used on crops: cucumbers, tomatoes, onions, cabbage, potatoes, grapes, vegetable peas.
Protects vegetable crops from diseases:
● cucumbers - false powdery mildew, anthracnose and powdery mildew;
● tomatoes - late blight, early blight and brown spot;
● onion - downy mildew, rot, fusarium wilt;
● cabbage - rot during storage;
● potatoes - late blight and early blight;
● grapes - mildew, oidium, gray rot, black spot;
● vegetable peas - downy mildew, powdery mildew and ascochitosis.
The image is two-color. An allotment is a plant with beautiful leaves that grows every year from a rhizome. It grows horizontally with or just below the surface. Growth requires warm and wet plant originated in the Philippines. However, it cannot be repainted, and the direct sun is not visible on its leaves. The blades of its leaves have long petioles. The leaves have a distinctive white vein and lower part of the bronchial bronchus.
Ideal for environment with high air humidity. Therefore, put it in a ceramic bowl and pour it into the bowl, the water evaporating from the expanded clay will humidify the air in its vicinity. If you roast your rhizomes on a new substrate every year, you don't need to plant or fertilize.
Methods of application: spraying plants. A package (6 ml) is diluted in 5 liters of water and used for spraying plants on an area of 1 weave.
12–14 days. The therapeutic effect is 2 days, which allows you to destroy the pathogen during the incubation period.
Waiting period: cucumbers, tomatoes - 5 days; potatoes, cabbage - 7 days, onions - 14 days. Let me remind you that the waiting period is the time after which you can use the plant for food after the last treatment. As you can see, Quadris is good because it has quite short term expectations.
Its large olive green leaves are silvery and gray striped between the veins. The underside has a burgundy grey colour. This species does not grow more than 30 cm, so it fits into smaller apartments. Since kaletey is cultivated in many species and different cultures, you can create a whole collection of them.
They need regular watering with water without calcium supplements. The xanthosome is closely related to the alocasia mentioned above. His appearance also applies to very interesting and unusual indoor plants. Unlike alocasia, its shoots do not die in winter. It bears arrow-shaped leaves on tall, elegant stems adorned with two black stripes. It is advisable to repot the plant every spring. Purple lovers certainly can't stand this spectacular plant, whose unusual leaf color evokes a large number of hair that is richly mature.
● cabbage - 1;
● onions, potatoes - 2;
● cucumbers, tomatoes - 3.
To avoid disease resistance to Quadris, you should not treat with this drug twice in a row, it is advisable to alternate treatments with other fungicides, for example, use Topaz and Ridomil Gold. Also, to reduce the risk of resistance of fungal diseases to Quadris, the drug can be used in a mixture with other fungicides.
Horus
Chorus is an effective fungicide against diseases such as scab, powdery mildew, moniliosis, curl, etc. A remarkable feature of chorus is its activity at low temperatures, it acts on pathogens even at a temperature of +5 ºС, which makes it possible to use it at the beginning of the growing season in period of bud break. It has translaminar and systemic action. Its use in stone fruit gardens has shown that it effectively protects trees from monilial scorch. It is also effective against various rots of fruits and berries.
It is applied on cultures: cherry, sweet cherry, apricot, plum, peach, apple-tree, pear, strawberry, grapes, lawn grasses.
● cherries, sweet cherries, apricots, plums - clasterosporiasis, monilial burn;
● apple, pear - scab, powdery mildew, fruit rot;
● strawberries - gray rot, powdery mildew, white and brown spots;
● grapes - oidium, gray rot, mildew;
● lawn grass - leaf spot.
Application methods: spraying plants.
● Cherry, sweet cherry, plum, apricot, apple, pear, peach: dilute 1 sachet (3 g) in 10 liters of water. Depending on the size of the tree, use 2-5 liters of working solution per plant.
● Strawberries: dilute 6 g in 5 liters of water and spray the plants before flowering and after harvesting at the rate of 5 liters per 1 hectare. After flowering, spraying should be carried out at the rate of 3 g per 5 liters of water, the consumption rate of the working solution is 5 liters per 1 hundred square meters.
● Grapes: dilute 6 g of the drug in 5 liters of water and treat 1 bush with 2 liters of working solution.
● Lawn grasses: dilute 6 g of the drug in 5 liters of water and spray the grass at the rate of 5 liters per 1 hundred square meters.
Duration of protective action: 10–12 days. The therapeutic effect is 2 days, which allows you to destroy the pathogen during the incubation period. Safe for bees, beneficial insects.
Waiting period: strawberries and grapes - 7 days, fruit crops - 30 days.
Maximum number of treatments per season:
●strawberry - 2;
● cherries, sweet cherries, plums, apricots, grapes - 3;
●apple, pear - 4.
Revus Top
Revus Top is a new fungicide for protecting potatoes and tomatoes from major diseases. The effectiveness of the drug increases due to the fact that it contains two active ingredients.
Mandiprolamide is partially absorbed by the leaf surface, and on both sides, part of the drug remains in the protective wax layer of the leaf. Thanks to this, the substance provides a long-term protective effect, moreover, it is resistant to washing off by precipitation.
The second active substance - difenoconazole - has a systemic effect, it is quickly absorbed and spread throughout the plant. Difenoconazole has a strong therapeutic effect, in addition, it has a preventive effect on Alternaria. In addition to the targeted effect on late blight and early blight, Revus Top has side effect, that is, it inhibits diseases such as rhizoctoniosis, septoria.
Used on crops: potatoes, tomatoes.
Protects crops from diseases: late blight and alternariosis.
Methods of application: spraying plants. Dilute 6 ml of the drug in 5 liters of water, respectively, 12 ml of the drug in 10 liters of water. Spray the plants with a working solution at the rate of 5 liters per 1 weave.
Duration of protective action: 14 days.
Waiting period: 14 days.
Ridomil Gold
Ridomil Gold is a combined drug of systemic and contact action. It has a translaminar and systemic action, thanks to which it protects not only leaves and stems, but also tubers, fruits, berries, being absorbed through the leaves and spreading throughout the plant. It has a healing and eradicating effect, therefore, even at the beginning of the development of the disease, when no more than 5% of plants are affected, it effectively protects potatoes and tomatoes. Also provides protection for potatoes during storage.
Used on crops: potatoes, tomatoes, cucumbers, grapes, onions (except for feathers), tobacco.
Protects crops from diseases: late blight, downy mildew, mildew.
Application methods: spraying plants. Dilute a 25 g package in 5 liters of water, respectively, dilute a 50 g package in 10 liters of water and spray the plants at the rate of 5 liters of working solution per 1 weave or 2 liters per grape bush. Tomatoes are sprayed with Ridomil Gold during the period of growth and budding.
Duration of protective action: 14 days.
Waiting period: cucumbers - 10 days, potatoes, tomatoes - 14 days, grapes - 25 days, onions - 30 days.
The maximum number of treatments per season is 3.
Important! To prevent the resistance of pathogens, it is recommended to alternate with other fungicides and not use more than two times in a row.
Thiovit Jet
Thiovit Jet - contact fungicide - acaricide for the protection of fruit crops and grapes from powdery mildew and mites. The active substance is finely ground sulfur in the form of granules, which, when released into water, form a stable suspension. Unlike colloidal sulfur, Thiovit Jet dissolves well in water and is better retained on the surface of treated plants.
It is used on crops: apple, pear, grapes, cucumbers, cabbage in greenhouses and greenhouses for soil disinfection, ornamental crops.
Methods of application: spraying.
● Apple and pear. Dissolve 40-80 g of the drug in 10 liters of water, treat the trees with a working solution at the rate of 2-5 liters per tree. Processing should be carried out prophylactically before flowering and after flowering with an interval of 10-14 days. In case of treatment, use a 0.5% solution (50 g of the drug per 10 liters of water).
● Prophylactically treat vineyards with a 0.5% solution twice before flowering with an interval of 8–10 days, at the first manifestations of the disease - also with a 0.5% solution with an interval of 8 days.
● Treat ornamental plants with a 0.5% solution at intervals of 10-14 days as needed.
Duration of protective action: 8-10 days.
Waiting period: 30 days.
Important! Sulfur refers to inorganic compounds, therefore it can be toxic to plants. To avoid toxic effects on plants, do not treat them on a wet leaf; do not mix with drugs that have an alkaline reaction; do not use the drug earlier than 14 days after using oil-based drugs.
Topaz
Topaz is a drug with selective, special action against powdery mildew. It has a strong therapeutic effect (3 days), prophylactically protects crops for 7-8 days. According to the mode of action, it belongs to systemic, translaminar drugs.
It is used on crops: cucumbers, black currants, apple trees, gooseberries, strawberries, raspberries, vineyards, ornamental crops.
Protects crops from diseases:
● cucumbers - powdery mildew;
● grapes - oidium;
● blackcurrant - powdery mildew, American powdery mildew;
● cherry - coccomycosis;
● peach - powdery mildew, fruit rot;
● apple tree, strawberry - powdery mildew;
● raspberries - purple spotting, gray rot.
Application methods:
● For open and protected ground cucumbers, dilute 6-8 ml of the drug in 10 liters of water. Use the working solution at the rate of 5 liters per 1 hundred square meters.
● For blackcurrant - 8-15 ml per 10 liters of water, 2 liters of solution per bush.
● For an apple tree - 10-15 ml per 10 liters of water, 2-5 liters of solution per tree.
● For gooseberries - 6 ml per 10 liters of water, 2 liters of solution per bush.
● For strawberries - 6-9 ml per 10 liters of water, 5 liters of solution per 1 hundred square meters.
● For raspberries (nurseries) - 6-8 ml per 10 liters of water, 1.5-2 liters per bush.
● For grapes - 6 ml per 10 liters of water, 1.5-2 liters per bush.
● Ornamental plants - 6-8 ml per 10 liters of water. Use the working solution at the rate of 5 liters per 1 hundred square meters.
Duration of protective action: 8-10 days.
Waiting period: 20 days.
Maximum number of treatments per season: 4.
Switch
Switch is a drug for protection against sulfur, fruit rot and other diseases. The drug is contact-penetrating and has a preventive and eradicating effect. It protects the plant at four stages of the development of the pathogen: during the germination of conidia, at the beginning of the growth of the pathogen mycelium, when the pathogen enters the plant cell, and also stops the growth of mycelium in the cell. The use of Switch significantly improves the keeping quality of fruits during storage and transportation. The therapeutic effect is two days, protective - 10-12 days. Safe for bees, beneficial insects.
It is used on crops: strawberries, pears, apricots, peaches, plums, cherries, tomatoes, cucumbers, roses, grapes, asparagus beans, vegetable peas.
Protects against diseases:
● Strawberries - gray rot, powdery mildew, white and brown spots;
● pear, apricot, peach, plum, sweet cherry - moniliosis, gray mold, fusarium rot, alternariosis, gray rot;
● tomatoes, cucumbers - gray rot, alternariosis, gray mold;
● roses - fusarium, alternaria and gray rot;
● grapes - gray rot;
● asparagus beans, vegetable peas - gray and white rot, ascochitosis.
Application methods:
● For strawberries, cucumbers, tomatoes, dilute 10 g of the drug in 5 liters of water. Use 5 liters of working solution per 1 weave.
● For pears, apricots, peaches, plums, sweet cherries, dilute 10 g of the drug in 10 liters of water. Use 2-5 liters of working solution per tree.
● For roses, grapes, asparagus beans, vegetable peas, dilute 10 g of the drug in 5-7 liters of water. Use 1.5–2 liters per bush, 5–7 liters per 1 weave.
Duration of protective action: 10–12 days.
Waiting period: strawberries - 7 days, tomatoes, cucumbers - 10 days, fruits - 15-20 days, roses - 15 days.
Maximum number of treatments per season: 2.
Speed
Skor is a systemic preparation for protecting fruits from scab, as well as peach from leaf curl. It has a strong therapeutic effect - up to 5 days and a long-term protective effect - 8-10 days. The biological activity of the drug depends little on weather conditions, which makes it even more convenient to use. Thanks to its therapeutic effect, it promotes the laying of healthy fruit buds, which ensures the next year's harvest. Thus, Skor not only preserves the harvest of the current year, but also increases the harvest of the next year, which increases its economic efficiency.
Used on crops: apple, pear, peach, potato, tomato, carrot.
Protects against diseases:
● apple tree, pear - scab, powdery mildew, alternariosis;
● peach - leaf curl;
● potatoes, tomatoes – Alternariosis, late blight;
● carrots - Alternariosis.
Application methods:
● Apple, pear, peach: dilute 2 ml of the drug in 10 liters of water and spray the trees at the rate of 2-5 liters of working solution per tree.
● Potatoes, tomatoes: dilute 2 ml of the drug in 5 liters of water and use 5 liters of working solution per 1 weave.
● Carrots: dilute 3-4 ml of the drug in 5 liters of water and use for spraying 1 weave.
Duration of the protective action: 10 days.
Waiting period: apple tree, pear - 30 days; potatoes, tomatoes, carrots - 14 days.
Maximum number of treatments per season: 3.
Important! When spraying varieties of apple trees that are severely affected by powdery mildew, Topaz or Horus must be added to Skor.
It should be noted that the treatment with fungicides, carried out not at the optimal time, when the plant is severely affected by the disease, as a rule, is already ineffective. In addition, the causative agents of many diseases remain on last year's foliage and plant debris, so their destruction and deliberate prevention is an important measure to maintain the health of your plants!